BY STEVEN MILLS
Specification plates found on cargo tank trucks provide emergency personnel with a variety of information at a hazardous materials incident involving these tanks. The information stamped on the specification plate identifies the type of cargo tank truck and its characteristics.
 1. Photos by author. |
null
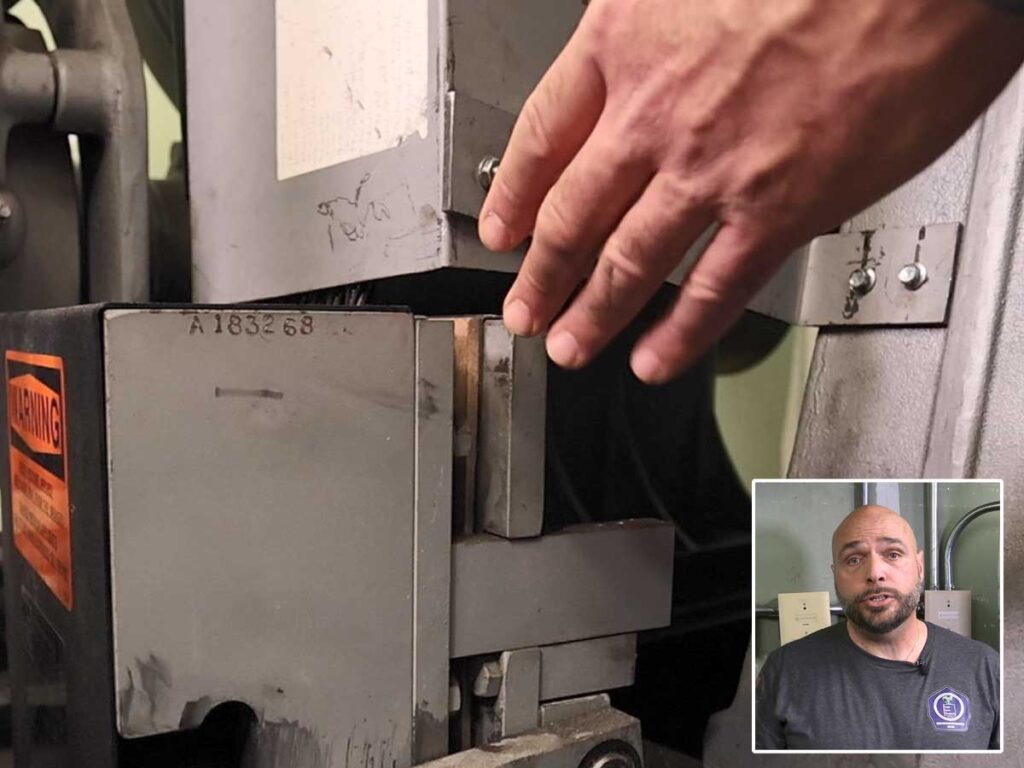
The specification plate’s primary purpose is to identify the suitability of the tanks for various chemicals that may be hauled and provide necessary repair information. The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) states that it is the manufacturer’s responsibility to certify that each tank has been designed, constructed, and tested in accordance with cargo tank truck requirements. Marking the cargo tank truck with a specification plate signifies the certification. Plates must be of corrosion-resistant material and permanently attached to the cargo tank truck or its integral supporting structure by brazing, welding, or other suitable means. Furthermore, the plates must be permanently and plainly marked in English by stamping or embossing. The standard also states that the plates must be affixed to the left side of the vehicle near the front of the cargo tank truck, in a place readily accessible for inspection (see photo 1). It’s worth noting that cargo tank trucks manufactured prior to July 1985 may have the specification plate on either side of the front third of the tank.
 2. |
null
Responders should be aware of the following information on the specification plate:
- Cargo tank truck specification number.
- Tank maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP), expressed in psig.
- Cargo tank truck design temperature range, expressed in degrees Fahrenheit.
- Nominal capacity in gallons (water capacity).
- Materials of construction.
- Cargo tank truck date of manufacture.
- Lining material (if applicable).
Although not all of the data stamped on the specification plate are useful to emergency personnel, some of the information can prove invaluable during an incident (see photo 2). The tank specification number positively identifies the type of cargo tank, such as MC 331, DOT 412, and so on. For liquid cargo tank trucks, specifications may include the current U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) specification series (406, 407, 412) or the older motor carrier (MC) specification series (MC 306, 307, 312). The DOT or MC marking indicates which specification the tank was designed to meet. The DOT standard, which became the mandatory standard for the manufacture of all cargo tank trucks on August 31, 1995, contains additional requirements for manufacturing quality control, structural integrity, and accident damage protection.
The cargo tank truck’s maximum allowable working pressure is listed as the “design pressure” and is expressed in psig. The design pressure provides a basis for comparison with the pressure gauge on the tank when this gauge is present. The closer the cargo tank truck’s pressure gauge reading is to the design pressure stamped on the specification plate, the greater the chance that a relief valve may activate.
This increasing pressure may indicate that the product in the tank is reacting with itself (polymerization) or is otherwise undergoing a reaction and that necessary precautions should be initiated. The tank’s “design temperature range” will warrant comparison with the tank temperature gauge, if one is present.
The cargo tank truck’s capacity is listed as “nominal capacity by compartment” and is listed from front to rear. This indicates the capacity in gallons of each compartment if there is more than one. Therefore, at a glance you will know the total capacity of the entire tank, how many compartments it has, and the capacity of each of these compartments.
If your incident involves transferring remaining product to an undamaged or “rescue” cargo tank truck, you must compare both cargo tank trucks’ specification plates. Pay close attention to “materials of construction” and “lining material” data. Diligence will ensure that a bad situation does not become disastrous when the product reacts with the lining or construction material of the rescue cargo tank truck.
Finally, the CFR allows for a “variable” specification plate. This style of plate is often found on cargo tank trucks that meet the DOT specifications for more than one type of cargo tank truck. Generally, on these types of cargo tank trucks, two specification plates may be adjacent to one another. A sliding metal plate on a track is used to completely cover one spec plate, thereby blocking its information from view; it can be secured in place. Regarding variable specification plates, the regulation states that only the plate identifying the applicable specification under which the tank is operating be legible.
Although specification plates are designed primarily as a reference for cargo tank truck repair and for determining its suitability for various chemicals or other materials, the information stamped on them is useful for emergency personnel. Becoming familiar with the plates and the information they provide can assist responders in making more informed decisions when operating at incidents involving cargo tank trucks.
STEVEN MILLS, a career lieutenant with the Ridge Road Fire District in Rochester, New York, has an associate’s degree in fire protection and is a nationally certified Fire Instructor I.