Talk-Back Cable TV Aids Training, Pre-Fire Planning
features
Modesto, Calif., Fire Department
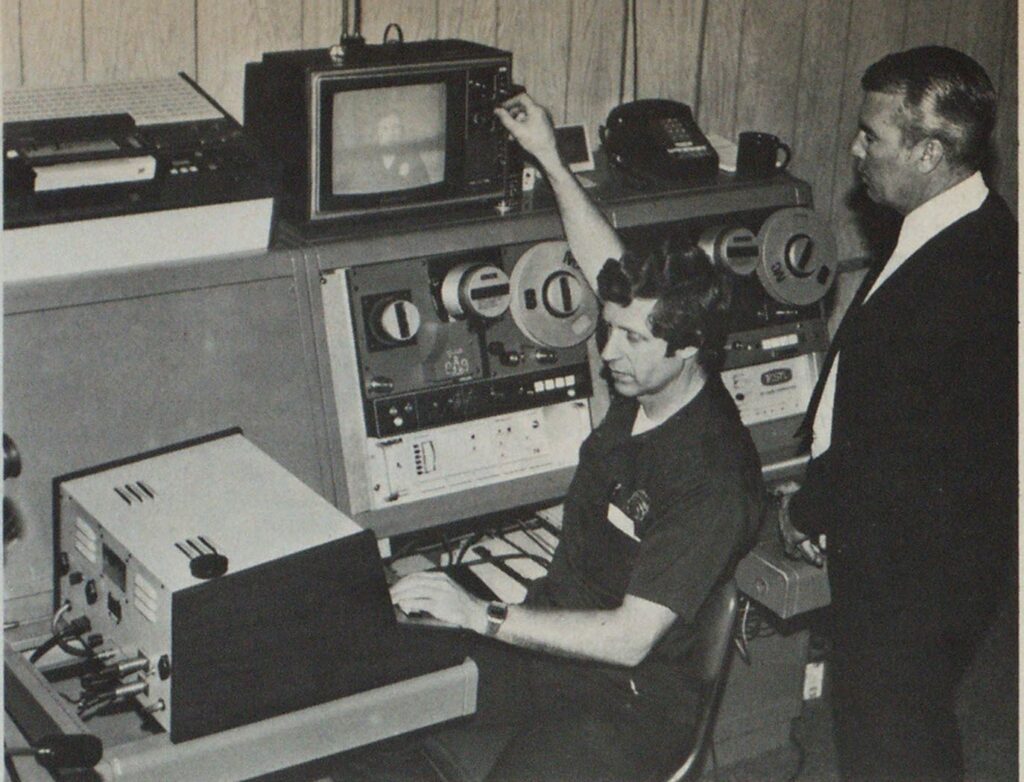
A cablevision system combined with a private telephone line that permits audience participation has solved a training problem in the Modesto, Calif., Fire Department.
Several years ago, it became evident that training personnel was becoming both increasingly difficult and timeconsuming. The city’s rapid growth in population and area indicated that the situation would become more critical.
Fire companies had to drive their rigs to the headquarters station for training. Occasionally, training was scheduled that required all on-duty companies to move to headquarters. This caused a significant increase in response time to alarm in the districts. In order to train all personnel, some sessions had to be given nine times. The fire department determined that the solution would be a television system which could allow participation from each of the outlying stations.
Private industry, local cablevision stations, and the Modesto Junior College television studio were contacted along with local library television personnel, the Federal Communications Commission and the Associated Public Safety Communications Offices. From these contacts, it was determined that general broadcast was too expensive and restrictive for one department. Likewise, microwave was too costly and shuttling video training tapes from station to station was too slow. Telephone did not provide quality video. One micro system, a special training channel allocation, was discussed, and although less costly than regular microwave, it was determined to be too expensive for the Modesto Fire Department.

The local cablevision station had the capability to carry both video and audio transmissions to all outlying fire stations if the department could provide them with a picture at their head end. Picture security could also be provided,but not audio security or talk-back capability.
System selected
After further investigation of the various alternatives, it was determined that the city would go to bid on a live or taped picture from the headquarters station inserted into a cable which goes to the cablevision station’s head end. That picture would then be distributed via a subchannel (for picture security) to all outlying fire stations. Each station would have a converter which makes the picture available on regular television sets.
The audio portion of the session would be sent out over a private looped telephone line which could be picked up at each station by an amplifier and speaker. By using a push-to-talk microphone which mutes program audio from the receiver, audience participation could be achieved. Training sessions could be held at the headquarters station and any personnel at the receiving fire stations could respond or ask questions of the instructors. All stations were to be able to participate at the same time.
Bids were opened Oct. 21,1975. The color system cost approximately $35,000 and went into limited service in 1977. In 1979, the Fire Department was assigned its own channel. Communicating with all personnel is now more efficient and effective. The television capability coupled with the delivery system is not only utilized in training and pre-fire planning, but also public education, officers meetings and taping actual fires.
Training activities
The following training is now taking place in the system:
- Training tapes are made to promote standardized methods for fire-ground operations.
- Individual and company drills are taped for critique and evaluation.
- Training movies are televised and special sessions at out-of-town seminars and workshops are taped and then disseminated over the system.
- In terms of pre-fire planning, the system is used to discuss in-depth plans and presentations, which are shared with the entire department at one time.
- Public education tapes for presentations to schools , service clubs and other groups can be made with the equipment used in the training system. The best of these programs can be shown over public or education channels.
- Actual fires are taped for critique, and modifications of attack techniques are then considered.
- Meetings via TV are held each morning by the on-duty battalion chief with all personnel at all stations to inform them of scheduled and completed activities, repair and maintenance, training, policy and procedural changes, annexations, water system improvements or weaknesses, and situations which could affect fire Fighting and response time.
- Fire prevention activities and arson investigation status reports are discussed.
The benefits of this television capacity and delivery system are many. The Modesto Fire Department has improved not only training, but also internal communications. There has been a decrease in fuel consumption and wear and tear on apparatus, and responses are not delayed as personnel remain at their own stations for training.